Stress is the body’s natural response to perceived challenges or threats. It triggers the “fight-or-flight” response, releasing hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, which prepare the body to respond to the situation. Stress can be acute (short-term), chronic (long-term), episodic acute (frequent short-term), eustress (positive stress), or distress (negative stress).
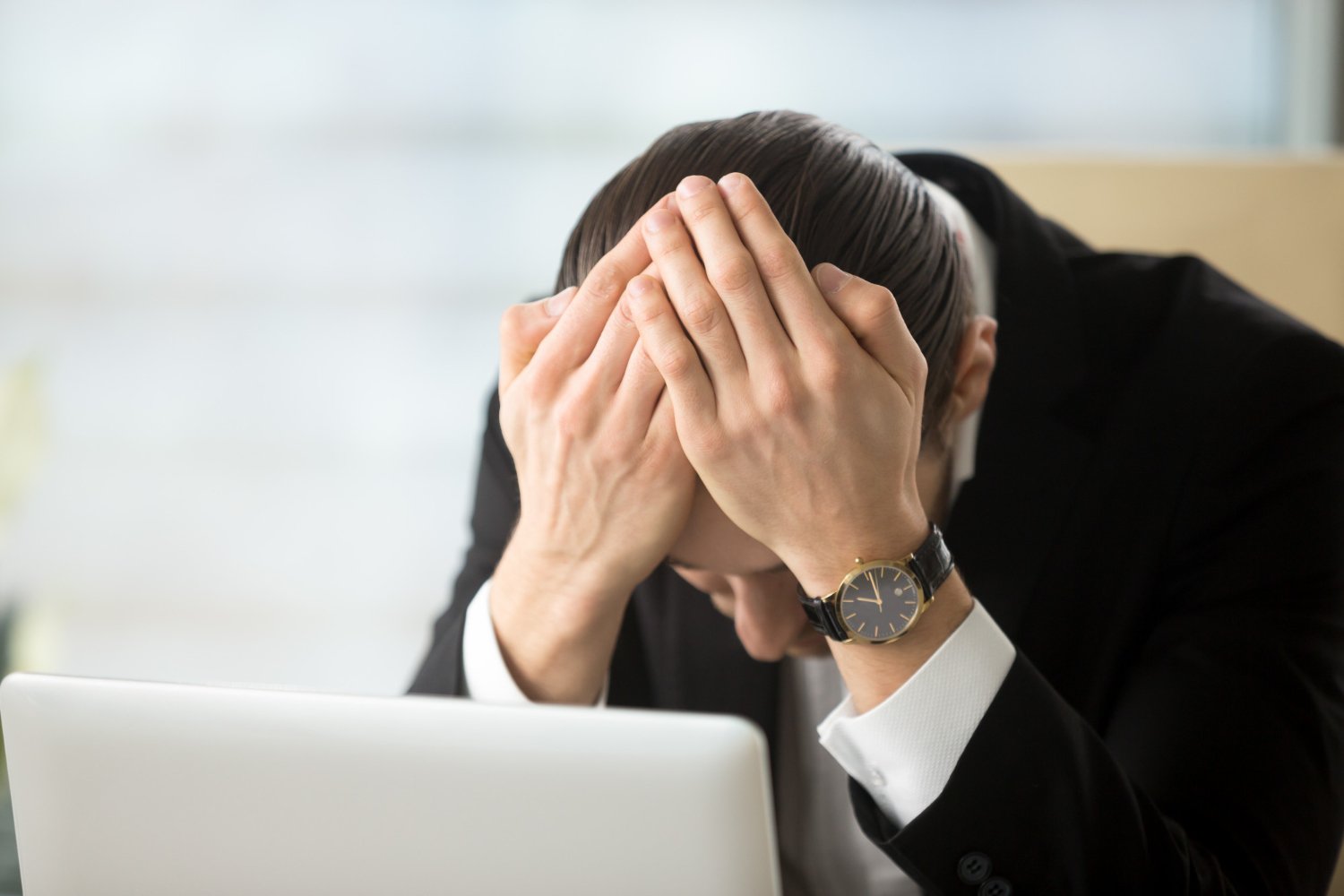

Common life stressors are events or situations that can cause significant stress and impact an individual’s mental and emotional well-being. Here are some of the most common life stressors:
The symptoms of stress can vary widely from person to person and can affect physical, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral aspects of well-being. Here are some common symptoms associated with stress:

Tension headaches or migraines.

Tightness or soreness, especially in the neck, shoulders, and back.

Persistent tiredness or exhaustion.

Insomnia, difficulty staying asleep, or oversleeping.
Upset stomach, nausea, diarrhea, or constipation.

Palpitations or feeling your heart racing.

Excessive sweating, particularly in the palms or underarms.

Overeating, undereating, or food cravings.
These symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, and experiencing them does not necessarily mean someone is under significant stress. However, if these symptoms persist and interfere with daily life, it may indicate that stress levels are too high and should be addressed.
Physical activity can help reduce stress by releasing endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
If you experience these symptoms frequently and they significantly interfere with your daily life, relationships, work, or school, it may be time to seek professional help. A mental health professional, such as a psychologist, psychiatrist, or counselor, can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Stress can be triggered by various external and internal factors. Common external causes include work-related pressures, financial problems, personal relationships, health issues, major life changes, and environmental factors. Internally, stress can be caused by personal expectations, negative thought patterns, certain personality traits, lifestyle choices, and inadequate coping mechanisms.
Work-related stress can result from job demands, long hours, job insecurity, conflicts with colleagues, or lack of career advancement opportunities. It can lead to physical symptoms like headaches, fatigue, and sleep disturbances, as well as emotional symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, and depression.
Yes, financial instability, debt, unexpected expenses, and lack of savings can all contribute to significant stress. Financial stress can manifest as physical symptoms like fatigue and digestive issues, and emotional symptoms like anxiety, depression, and irritability.
Common physical symptoms of stress include headaches, muscle tension, fatigue, sleep disturbances, digestive issues, increased heart rate, sweating, changes in appetite, and chest pain. These symptoms can vary in intensity and duration.
Stress can negatively impact mental health, leading to symptoms such as anxiety, depression, mood swings, difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and negative thinking. Chronic stress can exacerbate existing mental health conditions and lead to more severe issues over time.
Coping with stress can involve regular exercise, mindfulness and relaxation techniques, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, developing healthy coping mechanisms, building and maintaining social connections, engaging in hobbies, practicing gratitude, and taking breaks. It’s also important to limit exposure to stressors and practice problem-solving.
You can help by being a good listener, providing emotional support, offering practical help, encouraging healthy habits, respecting their boundaries, and being patient. Introducing them to relaxation techniques or suggesting they seek professional help can also be beneficial.
Adequate sleep is crucial for managing stress. Lack of sleep can exacerbate stress symptoms, such as irritability, difficulty concentrating, and physical fatigue. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night, and establish a consistent sleep routine to help manage stress.
Yes, lifestyle choices such as diet, exercise, sleep, and substance use can significantly impact stress levels. A balanced diet, regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine can help reduce stress.
If stress symptoms persist and interfere with your daily life, relationships, or work, it may be time to seek professional help. A therapist or counselor can provide guidance, support, and coping strategies to manage stress effectively.

Abha Healing Foundation